-
 Raian IonescuMaterial quality very good. we have cooperate more than 10 Years. They trade lots kinds of steel material. All material quality good. They duty for all material quality. We are planing continue cooperate with them in the future
Raian IonescuMaterial quality very good. we have cooperate more than 10 Years. They trade lots kinds of steel material. All material quality good. They duty for all material quality. We are planing continue cooperate with them in the future
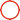
High Carbon 316H Stainless Steel Plate / UNS S31609 SS Plate Thickness 3.0 30.0mm Surface NO.1 2B
| Place of Origin | China |
|---|---|
| Brand Name | TISCO BAOSTEEL |
| Certification | ISO |
| Model Number | 316H / S31609 |
| Minimum Order Quantity | 500 kgs |
| Price | 5000 - 7200 USD/Ton |
| Packaging Details | standard packing for export |
| Delivery Time | 5 - 12 days based on the quantity |
| Payment Terms | T/T, Western Union |
| Supply Ability | 20Ton per week |
| Products | Stainless Steel Plate | Grade | 316H / S31609 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness | 0.6 - 30.0mm | Width | 1219mm 1500mm 1800mm 2000mm |
| Surface | NO.1 2B | Brand | BAOSTEEL TISCO |
| Standard | ASTM A240/240M | Loading Port | Shanghai Port |
| Highlight | High Carbon 316H Stainless Plate,UNS S31609 Stainless Steel Plate,S31609 SS Plate |
||
High Carbon 316H Stainless Steel Platee / UNS S31609 SS Plate Thickness 3.0 - 30.0mm
Products Specification
| Products Name | 317L Stainless Steel Plate |
| Main Grades | Stainless Steel J1, J2, J4, 201, 202, 301, 304, 304H, 304L, 309, 309S, 310, 310S, 316, 316L, 316TI, 317L, 321, 321H, 347, 409, 410, 410S, 420, 430, 441, 904L,630,631,254SMO,654SMO,253MA,2205,2507.etc |
| Thickness | 0.6 - 30.0mm |
| Width | 1250mm,1500mm ,1800mm,2000mm, or custom other size as request |
| Length | 2000mm, 2440mm, 3000mm, 5800mm, 6000mm, AS PER CUSTOMER’S REQUIREMENT |
| Type of Material | Laser Cutting |
| Form | Plate / coil |
| Test Certificate | Yes. |
| Finish | NO.1, 2B, 2D, 2H, 2R, No.4, HAIRLINE, SCOTCH BRITE, SATIN FINISH, NO.8, BA. |
| Brand | TISCO, LISCO,BAOSTEEL , POSCO, JISCO |
316H Stainless Steel: A High-Temperature Austenitic Alloy
1. Definition & Key Distinction:
316H is a high-carbon variant of the popular 316 austenitic stainless steel. The "H" suffix denotes its suitability for high-temperature service (typically above 500°C / 932°F), where enhanced strength is required.
2. Chemical Composition (Typical):
-
Carbon (C): 0.04–0.10% (Higher than standard 316/L to boost high-temperature strength).
-
Chromium (Cr): 16–18% (Provides oxidation/corrosion resistance).
-
Nickel (Ni): 10–14% (Maintains austenitic structure, improves ductility & corrosion resistance).
-
Molybdenum (Mo): 2–3% (Key for pitting/crevice corrosion resistance, especially in chlorides).
-
Manganese (Mn): ≤2%
-
Silicon (Si): ≤1%
-
Phosphorus (P): ≤0.045%
-
Sulfur (S): ≤0.03%
-
Iron (Fe): Balance
3. Key Properties & Advantages:
-
Excellent High-Temperature Strength: Superior creep strength (resistance to slow deformation under stress at high temps) compared to 316/L due to controlled higher carbon content.
-
Good Oxidation Resistance: Resists scaling in continuous service up to ~870°C (1600°F) and intermittent service up to ~925°C (1700°F).
-
Superior Corrosion Resistance: Inherits excellent general corrosion and pitting/crevice corrosion resistance from its base 316 chemistry, particularly in chloride environments (thanks to Molybdenum).
-
Austenitic Structure: Non-magnetic, good ductility, toughness, and formability in the annealed condition.
-
Fabricability: Can be readily welded and formed using standard methods for austenitic stainless steels (though post-weld annealing is often recommended).
4. Trade-offs:
-
Sensitization Risk: The higher carbon content increases susceptibility to sensitization (chromium carbide precipitation at grain boundaries) during welding or slow cooling through 425–815°C (800–1500°F). This can reduce corrosion resistance in the heat-affected zone. Solution annealing (rapid quenching from 1040–1150°C / 1900–2100°F) is crucial after high-temp exposure to dissolve carbides.
-
Lower Corrosion Resistance than 316L: In severely corrosive environments, especially after welding, standard 316L (low carbon) is often preferred to avoid sensitization issues.
5. Primary Applications:
316H is specifically engineered for demanding elevated temperature environments requiring both corrosion resistance and mechanical strength:
-
Power Generation: Boiler tubes, superheater tubes, heat exchangers, high-temperature piping in fossil fuel and nuclear plants.
-
Chemical & Petrochemical Processing: Furnace parts, catalyst grids, reactor vessels, piping handling hot corrosive fluids.
-
Heat Treating Equipment: Retorts, baskets, fixtures.
-
Oil & Gas Refining: High-temp piping and components.
-
Pressure Vessels designed for sustained high-temperature operation.
6. Common Specifications (Examples):
-
ASTM A213 / ASME SA213 (Seamless Ferritic and Austenitic Alloy-Steel Boiler, Superheater, and Heat-Exchanger Tubes)
-
ASTM A249 / ASME SA249 (Welded Austenitic Steel Boiler, Superheater, Heat-Exchanger, and Condenser Tubes)
-
ASTM A312 / ASME SA312 (Seamless and Welded Austenitic Stainless Steel Pipes)
-
ASTM A358 / ASME SA358 (Electric-Fusion-Welded Austenitic Chromium-Nickel Stainless Steel Pipe for High-Temperature Service)
-
UNS S31609
7. Comparison Summary:
-
vs. 316: Higher carbon (0.04-0.10% vs. max ~0.08%) for better high-temp strength.
-
vs. 316L: Significantly higher carbon (316L max is 0.03%) for strength at temp, but greater sensitization risk. 316L excels where welding or maximum corrosion resistance is critical.
-
vs. 316Ti/321: 316H relies on carbon for strength; 316Ti/321 use Titanium or Niobium to stabilize against sensitization (better for welded corrosive service, but may have slightly lower creep strength at very high temps).
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()