-
 Raian IonescuMaterial quality very good. we have cooperate more than 10 Years. They trade lots kinds of steel material. All material quality good. They duty for all material quality. We are planing continue cooperate with them in the future
Raian IonescuMaterial quality very good. we have cooperate more than 10 Years. They trade lots kinds of steel material. All material quality good. They duty for all material quality. We are planing continue cooperate with them in the future
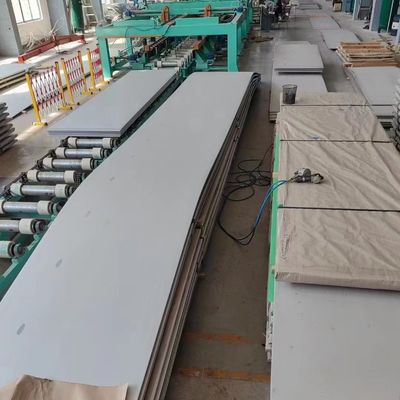
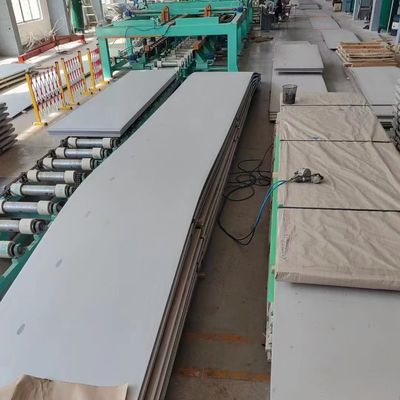
CNC Laser Cutting ASTM A240 Stainless Steel Plate 310S 316L 321 410 420 430 431
| Place of Origin | China |
|---|---|
| Brand Name | TISCO BAOSTEEL |
| Certification | ISO |
| Model Number | 201 304 316L 321 310S 347 410 420 430 431.etc |
| Minimum Order Quantity | 500 kgs |
| Price | 2100-5300 USD/Ton |
| Packaging Details | standard packing for export |
| Delivery Time | 5 - 12 days based on the quantity |
| Payment Terms | T/T, Western Union |
| Supply Ability | 20Ton per week |

Contact me for free samples and coupons.
Whatsapp:0086 18588475571
Wechat: 0086 18588475571
Skype: sales10@aixton.com
If you have any concern, we provide 24-hour online help.
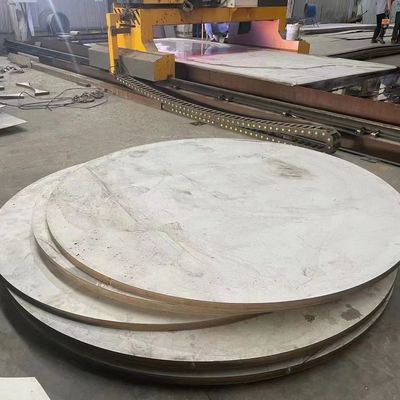
x| Products | Stainless Steel Plate | Grade | 201 304 316L 310S 321 2205 2507.etc |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness | 3.0-100.0mm | Width | 1500mm 1219mm 1000mm |
| Surface | NO.1 2B | Brand | TISCO |
| Standard | ASTM A240/240M | Loading Port | Shanghai Port |
| Highlight | CNC Laser Cutting Stainless Steel Plate,ASTM A240 Stainless Steel Plate,431 Stainless Steel Plate |
||
CNC Laser Cutting ASTM A240 Stainless Steel Plate Grade 201 304 310S 316L 321 410 420 430 431
Our Stainless Steel Sheet Specification Chart
| Description | ASTM A240 / ASME SA240 Stainless Steel Plates, ASTM A240 Hot Rolled Stainless Steel Plates |
| Standard | ASTM, ASME, BS, DIN, EN |
| Material | 310S, 310, 309, 309S, 316, 316L, 316Ti, 317, 317L, 321, 321H, 347, 347H, 304, 304L, |
| 302, 301, 201, 202, 403, 405, 409, 409L, 410, 410S, 420, 430, 631, 904L, Duplex, etc | |
| Specification | Cold rolled: 1219mm * 2438mm (4′ x 8′), 1219mm * 3048mm (4′ x 10′), 1220mm * 2440mm, 1250mm * 2500mm or as your requirement.
Hot rolled: 1500mm * 2000mm, 1000mm * 3000mm, 1500mm * 4000mm, 1500m * 6000mm or as your requiremnt. |
| Technique | Hot rolled plate (HR), Cold rolled sheet (CR), 2B, 2D, BA NO(8), SATIN (Met with Plastic Coated) |
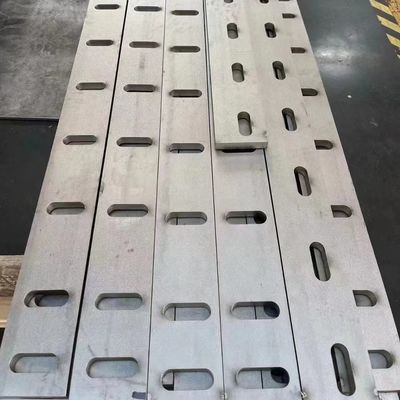
| Form | Shim Sheet, Perforated Sheet, Chequered Plate, Strip, Flats, Etc. |
| Surface | 2B, 2D, BA, NO. 1, NO. 4, NO.8, 8K, Mirror, Checkered, Embossed, Hair Line, Sand Blast, Brush, Etching |
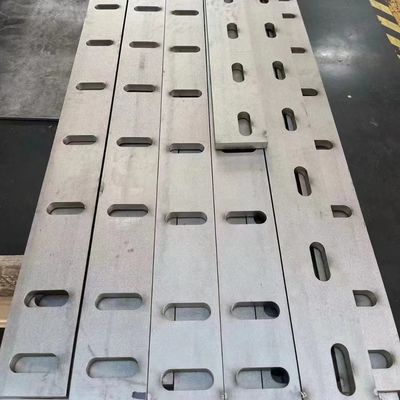
| Service | Laser Cutting, Water Cutting, Fire Cutting, Bending |
| Thickness | 0.25-200mm, 0.3mm to 120mm |
| Width | 1000mm, 1219mm, 1500mm, 1800mm, 2000mm, 2500mm, 3000mm, 3500mm |
| Length | 2000mm, 2440mm, 3000mm, 5800mm, 6000mm, 12000mm |
| Package | Standard Export Seaworthy Package, or as required. |
| Value Added Services | Cladding,Heat Treatment,Annealed, Pickling, Polish,Rolling,Cutting,Bending,Forging,Minor Fabrication Etc. |
| MTC | Mill Test Certificate, Available as per EN 10204 3.1 |
What Is Stainless Steel?
Stainless steel is a broad term for austenitic, ferritic, precipitation, martensitic, and duplex (those with both austenitic and martensitic components) alloys. These alloys contain iron, carbon, chromium, and a range of other metallic alloying agents such as: nickel, molybdenum, copper, niobium, titanium, and aluminum. Intentional additions can also be non-metallic, such as: silicon, carbon, and sulfur.
The result is a spectrum of properties. Some alloys are strongly magnetic while others are only weakly so or entirely non-magnetic. Some such steels are easy to work-harden while others barely change. And though “stainless steel” is rhetorically synonymous with corrosion resistance, some versions actually do not fare well on that front.
What Are the Types of Laser Cuttable Stainless Steel?
All stainless steel alloys can be laser-cut given the proper machine settings, sufficient power, and the right controlled atmosphere. In general, the types of cuttable stainless steels are:
- Austenitic Stainless Steel: These steels have a face-centered cubic structure. They cannot be heat treated and they’re non-magnetic. The austenitic structure of the 300 series comes from the high nickel content whereas, in the 200 series, it is an effect of manganese and nitrogen in the structure. They are highly corrosion-resistant and work-harden to various degrees.
- Martensitic Stainless Steel: Martensitic stainless steel can come in high or low-carbon varieties. They can all be hardened and tempered by heat/quench processes. Classed as 400 series, they are generally less tough than austenitic steels and offer lower corrosion resistance. However, they are considerably more machinable because of their lower nickel content and a lower tendency to work harden.
- Ferritic Stainless Steel: This is a subgroup of the 400 series. These materials are heat-treatable and harden without putting in too much work. Examples are 430 stainless steel, often referred to as blade steel. They don’t tolerate cryogenic conditions but retain their properties at high temperatures. Additionally, they're not weldable.
These three families of materials are distinct in properties such as: work hardening, magnetic permittivity, corrosion resistance, hardness, and crystalline structure.
What Lasers Can Do to Stainless Steel?
Laser cutting offers significant advantages over other 2D processing methods when working with stainless steel. The technology involves no force or distortion, so it does not induce any work hardening. Laser cutting, when performed under optimal conditions, produces fused, fairly smooth edges that rarely need post-processing. Cuts as deep as 100 mm are possible in a single pass which allows fast processing of large items.
Laser marking of stainless steel comes in two forms: straightforward ablation and laser annealing. Laser ablation is the process by which material is vaporized and removed. Laser annealing, on the other hand, is where the chromium oxide surface is largely undisturbed; instead, the metal beneath is annealed or melted and a limited amount of oxidation takes place below the outer oxide film. The latter method makes cleaner markings but it requires considerable skill to do it without ablating some material away. The low (highly localized) heating of the target area results in little or no distortion and staining in the wider heat-affected zone (HAZ). By contrast, rapid rotating cutter machining can alter hardness considerably around the cut zone and can result in heat distortion and discoloration over wider areas.
Laser engraving of stainless steel is possible as well, but it often results in discoloration. The engraving process destroys some of the surface oxide layers. Laser engraving is functionally identical to laser cutting. The difference is that the cut depth must be very tightly controlled to achieve good surface quality.
Laser etching is a more controlled process for stainless steel. The subsurface of unoxidized metal is annealed or melted without removing the protective oxide surface layer, which is essentially transparent to most cutting lasers. This method allows limited diffusion of oxygen through the oxide layer, staining the metal below in shades of yellow or brown depending on the intensity. This process is sometimes referred to as laser annealing.
What Kind of Laser Can Effectively Cut Stainless Steel?
The lasers that can effectively cut stainless steel are fiber and CO2 lasers. Fiber lasers can produce much narrower beams — typically half the diameter of the cutter ‘dot’ of a CO2 laser. This results in about quadruple the effective power for the same laser output energy. Fiber lasers can process faster and with greater precision because of this. Operating costs for fiber lasers are lower because of their electrical efficiency (4 to 6 times better than for CO2 devices) and solid-state construction. They do require more nitrogen shielding gas in the cutting process, though.
CO2 laser cutting typically delivers a 600-µm cutter beam width. These lasers are capable of much higher device power than fiber lasers, though modern fiber lasers are gaining ground in that regard. CO2 lasers are better suited to lower-precision cuts on thicker parts. The CAPEX cost of equipment is considerably lower than for fiber laser machines, but OPEX costs are higher per length of cut.
What Is the Difference Between CO2 and Fiber Laser for Laser Cutting Stainless Steel?
CO2 lasers offer coarser beams than fiber lasers. However, CO2 lasers are capable of delivering considerably higher power in the 100+ kW power range. These lasers are cheaper but have higher maintenance costs than fiber lasers. Fiber lasers have limited power (15-20 kW), but can cut considerably faster than CO2 laser machines (3 to 5 times the feed speed), because their narrower beam means higher effective energy at the cut point.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()