-
 Raian IonescuMaterial quality very good. we have cooperate more than 10 Years. They trade lots kinds of steel material. All material quality good. They duty for all material quality. We are planing continue cooperate with them in the future
Raian IonescuMaterial quality very good. we have cooperate more than 10 Years. They trade lots kinds of steel material. All material quality good. They duty for all material quality. We are planing continue cooperate with them in the future
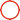
ASTM A240 Type 316L Stainless Steel Strip and SS 316L Coil EN 1.4404 Stainless Steel
| Place of Origin | China |
|---|---|
| Brand Name | TISCO |
| Certification | ISO |
| Model Number | 316L / 1.4404 / SUS316L |
| Minimum Order Quantity | 500 kgs |
| Price | 2388 - 3660 USD/Ton |
| Packaging Details | standard packing for export |
| Delivery Time | 5 - 12 days based on the quantity |
| Payment Terms | L/C, T/T, Western Union |
| Supply Ability | 20Ton per week |
| Products | Stainless Steel Strip | Thickness | 0.1-3.0mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Width | Within 1500mm | MOQ | 500 Kgs |
| Grade | 200 Series 300 Series 300 Series | Surface | BA 2B NO.4 HL 8K NO.1 2D |
| Standard | ASTM EN GB JIS | Packing | Wooden Frame And Water Proof Paper |
| Highlight | steel strip coil,stainless steel coil strip,decorative stainless steel strips |
||
ASTM A240 Type 316L Stainless Steel Strip and SS 316L Coil EN 1.4404 Stainless Steel
| Product Name | Stainless Steel Strips |
| Length | As required |
| Width | 3mm-1219mm or as required |
| Thickness | 0.1 - 3.0mm or as required |
| Standard | AISI,ASTM,DIN,JIS,GB,JIS,SUS,EN,etc. |
| Technique | Hot rolled / cold rolled |
| Surface Treatment | 2B or according to customer requirement |
| Thickness tolerance | ±0.01mm |
| Material | 201, 202, 301, 302, 303, 304, 304L, 304H, 310S, 316, 316L, 317L, 321,310S 309S, 410, 410S,420, 430, 431, 440A,904L |
| MOQ | 1tons.We also can accept sample order. |
| Shipment time | Within 15-20 workdays after receiving deposit or L/C |
| Export packing | Waterproof paper, and steel strip packed.Standard Export Seaworthy Package.Suit for all kinds of transport,or as required |
| Capacity | 2500 tons/year |
316L Stainless Steel: Composition, Properties
- 316L stainless steel is an austenitic stainless steel that belongs to the standard CrNiMo stainless steels, the “L” at 316L stainless steel grade stands for low carbon(≤0.030%), the low carbon version of 316, and derivative steel 18-8 type stainless steel adding 2 ~ 3% of molybdenum element, which enhances its corrosion resistance, 316L is molybdenum-bearing grade.
- 316L stainless steel is second wide used Austenitic stainless steel due to its excellent properties, the austenitic structure also gives 316L excellent toughness, even down to cryogenic temperatures, grade 316L has low carbon content for improved resistance against intergranular corrosion after welding, compared to chromium-nickel austenitic stainless steels, 316L stainless steel with molybdenum content added offers higher creep, stress to rupture and tensile strength at elevated temperatures., The higher nickel and molybdenum content in this grade allows it to demonstrate better overall corrosion-resistant properties than 304, especially with regard to pitting and crevice corrosion in chloride environments.
316L Stainless Steel Features And Advantages
- The second-most widely used stainless steel grade after stainless steel 304
- Molybdenum-bearing grade
- It is non-magnetic stainless steel in the annealed condition.
- It is marine-grade stainless steel
- Aka, AISI 316L, TP316L, , SUS316L, SS316L, 316L SS, UNS S30603
- More forms and finishes
- It can be used in most conditions due to its excellent properties
316L Stainless Steel Chemical Composition
The chemical composition of stainless steel 316L is generally composed of 16 to 18% chromium, 10 to 14% nickel, 2 to 3% molybdenum, and a small percentage of carbon(≤0.030%), adding molybdenum to stainless steel 316L increases its corrosion resistance compared to other grades of stainless steel.
| Standard | Grade | C | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo | N | Iron |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASME II A SA-240 | 316L | ≤0.030 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.030 | 16.0-18.0 | 10.0-14.0 | 2.00-3.00 | ≤0.10 | Bal. |
| ASTM A240 | 316L | ≤0.030 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.030 | 16.0-18.0 | 10.0-14.0 | 2.00-3.00 | ≤0.10 | Bal. |
| EN 10088-2 | 1.4404 | ≤0.030 | ≤2.0 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.030 | 16.5-18.5 | 10.0-13.0 | 2.0-2.5 | ≤0.10 | Bal. |
The chemical composition is given as % by mass.
Compared to 316, 316L, 1.4401, 1.4404, 1.4435 in chemical composition
| C | Mn | P | S | Si | Ni | Cr | Mo | N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 316 | 0.08 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 11-14 | 16-18 | 2-3 | |
| 316L | 0.035 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 10-14 | 16-18 | 2-3 | |
| 1.4401 | 0.07 | 2.00 | 0.040 | 0.015 | 1.0 | 10-13 | 16.5-18.5 | 2-2.5 | 0.11 |
| 1.4404 | 0.03 | 2.00 | 0.040 | 0.015 | 1.0 | 10-13 | 16.5-18.5 | 2-2.5 | 0.11 |
| 1.4435 | 0.03 | 2.00 | 0.040 | 0.015 | 1.0 | 12.5-15 | 17-19 | 2.5-3 | 0.11 |
Note: SUS316L is JIS standard grade, Ni content 12% – 15%.
316L Stainless Steel Mechanical Properties
| Standard | Grade | Yield Point | Tensile Strength | Elongation | Hardness | Hardness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPa | MPa | % | HRB | HB | ||
| ASME II A SA-240 | 316L | ≥ 170 | ≥ 485 | ≥ 40 | ≤ 95 | ≤ 217 |
| ASTM A240 | 316L | ≥ 170 | ≥ 485 | ≥ 40 | ≤ 95 | ≤ 217 |
| EN 10028-7 | 1.4404 | ≥ 240 | 530-680 | ≥ 40 | ||
| EN 10088-2 | 1.4404 | ≥ 240 | 530-680 | ≥ 40 | ||
| EN 10088-4 | 1.4404 | ≥ 240 | 530-680 | ≥ 40 |
Compared To 316, 316L 1.4401, 1.4404, 1.4435
| Tensile Strength(Mpa) | Yield Point(Mpa) | Elongation(%) | Hardness (HRB) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 316 | 515 | 205 | 35 | 95 |
| 316L | 485 | 170 | 35 | 95 |
| 1.4401 | 510-710 | 205 | 40 | 95 |
| 1.4404 | 490-690 | 190 | 40 | 95 |
| 1.4435 | 490-690 | 190 | 40 | 95 |
316L Stainless Steel Equivalent Grades
| AISI | UNS | DIN | EN | JIS | GB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 316L | S31603 | 1.4404 | X2CrNiMo17-12-2 | SUS316L< | 022Cr17Ni12Mo2 |
316L Stainless Steel Physical Properties
| Density | Melting Point | Specific Heat | Thermal Conductivity | Coefficient Of Expansion | Electrical Resistivity | Elastic Modulus | Magnetic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G/Cm3 | ( ℃ ) | [J/(Kg·K)] 0~100 ℃ | W/(M·K) | 10-6/K | (NΩ.M | KN/Mm2 | |
| 7.99 | 1398~1427 | 500 | 16.3 At 100 ℃ | 16.6 At 0~100 ℃ | 740 | 193 | A Little After Cold Worked |
| 21.5 At 500 ℃ | 18.6 At 0~500 ℃ |
316L Stainless Steel Variants
Due to 316L’s excellent properties, 316L is expended in some other grades for various applications, developing other stainless steels by adding different chemical elements, such as adding a small amount of Ti derived after 316Ti, which offers better resistance to intergranular corrosion, adding a small amount of N derived from 316N, increasing the content of Ni and Mo derived 317.
| Grade | Alloying Elements (Percent) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Cr | Ni | Mo | Mn | Si | N | P | S | Others | |
| 316 | 0.08 | 16-18 | 10-14 | 2-3 | 2.0 | 0.75 | 0.10 | 0.045 | 0.03 | |
| 316L | 0.03 | 16-18 | 10-14 | 2-3 | 2.0 | 0.75 | 0.10 | 0.045 | 0.03 | |
| 316H | 0.04 – 0.10 | 16-18 | 10-14 | 2-3 | 2.0 | 0.75 | 0.045 | 0.03 | ||
| 316Ti | 0.08 | 16-18 | 10-14 | 2-3 | 2.0 | 0.75 | 0.10 | 0.045 | 0.03 | Ti, 5 X (C + N)-0.70% |
| 316Cb | 0.08 | 16-18 | 10-14 | 2-3 | 2.0 | 0.75 | 0.10 | 0.045 | 0.03 | Cb, 10 X (C + N)-1.10% |
| 316N | 0.03 | 16-18 | 10-14 | 2-3 | 2.0 | 0.75 | 0.10 – 0.16 | 0.045 | 0.03 | |
| 316LN | 0.03 | 16-18 | 10-14 | 2-3 | 2.0 | 0.75 | 0.10 – 0.16 | 0.045 | 0.03 | |
Corrosion Resistance
316L/4404 has excellent corrosion resistance in solutions of many halogen-free organic and inorganic compounds over a wide temperature and concentration range.
- It is a better choice than 304 in a range of atmospheric environments and many corrosive media due to the increased chromium and molybdenum content.
- Resist pitting and crevice corrosion in warm chloride environments, and stress corrosion cracking above about 122°F (50°C).
- Considered resistant to potable water with up to about 1000mg/L chlorides at ambient temperatures, reducing to about 500mg/L at 140°F (60°C).
- Usually regarded as marine-grade stainless steel, but is not resistant to warm sea water.
Heat Resistance
With good oxidation resistance in intermittent service to 870 °C and in continuous service to 925 °C, Grade 316L stainless steel is more resistant to carbide precipitation.
Good oxidation resistance in intermittent service to 870 °C and in continuous service to 925 °C. Continuous use of 316 in the 425-860 °C range is not recommended if subsequent aqueous corrosion resistance is important. Grade 316L is more resistant to carbide precipitation and can be used in the above temperature range. Grade 316H has higher strength at elevated temperatures and is sometimes used for structural and pressure-containing applications at temperatures above about 500 °C.
Welding Characteristic
Excellent weldability by all standard fusion methods, both with and without filler metals, Heavy welded sections in Grade 316 require post-weld annealing for maximum corrosion resistance, this is not required for Grade 316L.
Heat Treatment And Hardening
316L annealing temperature range is 1900 to 2100°F (1038 to 1149°C), cannot be hardened by heat treatment, It can be hardened by cold working.
Machining
316L stainless steel tends to work harden if machined too quickly. For this reason, low speeds and constant feed rates are recommended.
316L stainless steel is also easier to machine compared to 316 stainless steel due to its lower carbon content.
Differences Between 316 And 316L
316L is very similar to 316 in almost every aspect. They are both durable, corrosion-resistant, and a good choice for high-stress applications, in practice, dual-certified grade 316/316L is often required.
However, the “L” designation means 316L steel has less carbon than 316 steel, it is less susceptible to sensitization, a condition caused when carbon combines with chromium around the grain boundaries, depleting the grain boundary areas of chromium during the welding process, though it can be resisted via annealing.
Chemical Properties Comparison
| C | Mn | Si | P | S | Cr | Mo | Ni | N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 316 (S31600) |
0.08 Max |
2.0 Max |
0.75 Max |
0.045 Max |
0.03 Max |
Min: 16.0 Max: 18.0 |
Min: 2.0 Max: 3.0 |
Min: 10.0 Max: 14.0 |
0.10 Max |
| 316L (S31603) |
0.03 Max |
2.0 Max |
0.75 Max |
0.045 Max |
0.03 Max |
Min: 16.0 Max: 18.0 |
Min: 2.0 Max: 3.0 |
Min: 10.0 Max: 14.0 |
0.10 Max |
Mechanical Properties Comparison:
| Grade | Tensile Strength Ksi (Min) |
Yield Strength 0.2% Ksi (Min) |
Elongation % | Hardness (Brinell) MAX | Hardness (Rockwell B) MAX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 316 (S31600) |
75 | 30 | 40 | 217 | 95 |
| 316L (S31603) |
70 | 25 | 40 | 217 | 95 |
316L Stainless Steel Forms
- Sheet
- Strip
- Bar
- Plate
- Pipe
- Tube
- Coil
- Fittings
Related References
- ASTM A240/ASME SB240, Standard Specification for Chromium and Chromium-Nickel Stainless Steel Plate, Sheet, and Strip for Pressure Vessels and for General Applications
- ASTM A480, Standard Specification for General Requirements for Flat-Rolled Stainless and Heat-Resisting Steel Plate, Sheet, and Strip
- EN 10088-2, Stainless steels. Technical delivery conditions for sheet/plate and strip of corrosion-resisting steels for general purposes
- EN 10088-3, Stainless steels. Technical delivery conditions for semi-finished products, bars, rods, wire, sections and bright products of corrosion-resisting steels for general purposes
- EN 10088-4, Stainless steels. Technical delivery conditions for sheet/plate and strip of corrosion-resisting steels for construction purposes
- EN 10088-5, Stainless steels. Technical delivery conditions for bars, rods, wire, sections and bright products of corrosion-resisting steels for construction purposes
- ASTM A249, Standard Specification for Welded Austenitic Steel Boiler, Superheater, Heat-Exchanger, and Condenser Tubes
- ASTM A213, Standard Specification for Seamless Ferritic and Austenitic Alloy-Steel Boiler, Superheater, and Heat-Exchanger Tubes
- ASTM A312, Standard Specification for Seamless, Welded, and Heavily Cold Worked Austenitic Stainless Steel Pipes
- ASTM A276, Standard Specification for Stainless Steel Bars and Shape
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()