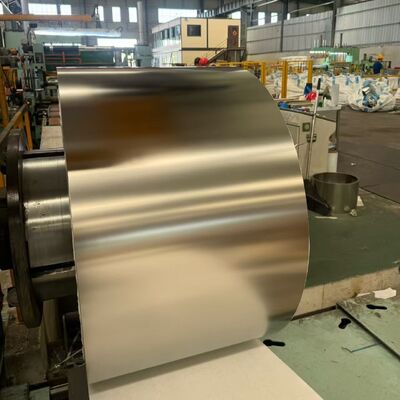
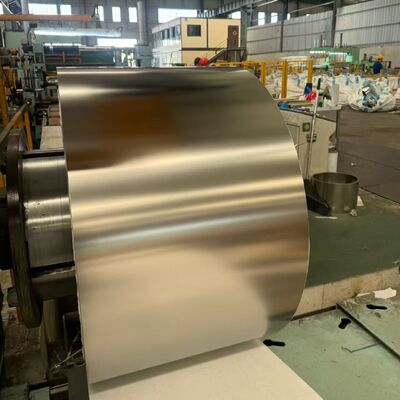
식품 및 의료 분야를 위한 고정밀 316L/1.4404/SUS316L 스테인레스 스틸 스트립 0.1mm - 3.0mm
제품 사양
| 제품 |
스테인레스 스틸 스트립 |
| 두께 |
0.1-3.0mm |
| 너비 |
최소 너비 5mm |
| MOQ |
20kg |
| 주요 학년 |
201 301 304 304L 309S 310S 316L 316Ti 410 420 430 436 439 441 444 440A/B/C,2205,2507,904L,C276,400,600,625,926,825.etc |
| 표면 |
학사 2B |
| 기준 |
ASTM EN GB JIS |
| 포장 |
나무 프레임과 방수 종이 |
JIS G4305 SUS304 스테인레스 스틸 스트립 두께 0.1 - 3.0mm – 스프링 응용 분야를 위한 정밀 슬릿 커팅 엣지 제품 개요 JIS G4305:2021 표준을 엄격히 준수하여 제조된 SUS304 스테인레스 스틸 스트립은 정밀 엔지니어링 및 산업 응용 분야에서 가장 널리 사용되는 오스테나이트 스테인레스 스틸 등급 중 하나입니다. 0.1mm ~ 3.0mm의 두께 범위를 갖는 이 냉간 압연 스트립은 정밀 슬릿 커팅 엣지로 특수 가공되어 스프링, 커넥터, 단자, 전자 부품과 같은 고성능 부품에 이상적입니다. SUS304(국제적으로 AISI 304 또는 UNS S30400이라고도 함)는 내식성, 성형성, 용접성 및 기계적 강도의 탁월한 균형을 제공합니다. 일반적으로 크롬 18%와 니켈 8%로 구성된 이 제품은 식품 가공, 의료 기기, 자동차 시스템, 가전제품 등 주변 환경과 약간 공격적인 환경 모두에서 탁월한 성능을 보장합니다. 이 제품 페이지는 신뢰할 수 있고 내구성이 뛰어난 스테인레스 스틸 스트립 소재를 찾는 엔지니어, 조달 전문가 및 제조업체를 위한 포괄적인 기술 사양, 화학 성분, 기계적 특성 및 적용 지침을 제공합니다. 주요 특징 및 장점 ✅ 규정 준수: JIS G4305:2021(냉간 압연 스테인레스 강판, 시트 및 스트립)을 완전히 준수합니다. ✅ 정밀 슬리팅: 가장자리 공차 ±0.01mm; 자동화된 조립을 위한 버 없는 마감 ✅ 두께 범위: 0.1mm – 3.0mm(요청 시 맞춤 설정 가능) ✅ 폭 옵션: 5mm – 600mm(표준); 마이크로 스프링 응용 분야에 사용 가능한 좁은 폭 ✅ 표면 마감: 2B, BA(광택 소둔) 또는 맞춤형 마감(예: 헤어라인, 무광택) ✅ 우수한 스프링 특성: 높은 피로 저항 및 반복 편향 후 탄성 회복 ✅ 부식 저항: 최대 800°C까지 산화 저항; 습하고 염분 및 약산성 환경에 적합 ✅ 비자성(어닐링 상태): 민감한 전자 및 의료 기기에 이상적 기술 사양 매개변수 사양 표준 JIS G4305:2021 재료 등급 SUS304(일본 산업 표준) 등가 등급 AISI 304(USA), X5CrNi18-10(EN), 1.4301(DIN), 06Cr19Ni10 (GB/T) 형태 냉간 압연 스테인레스 스틸 스트립 두께 범위 0.1mm – 3.0mm 폭 범위 5mm – 600mm(±0.05mm 공차의 정밀 슬릿) 공차(두께) ±0.005mm(<0.5mm의 경우); ±1%(≥0.5mm의 경우) 가장자리 상태 정밀 슬릿, 디버링됨, 가장자리 균열 없음 표면 마감 2B(표준), BA(광택 소둔), HL(헤어라인) 또는 고객 지정 열처리 조건 소둔(연질), 1/4H, 1/2H, H, EH, SH(스프링 템퍼 사용 가능) 밀도 7.93 g/cm3 자기 특성 소둔 상태에서는 비자성입니다. 냉간 가공 후 약간의 자성을 띌 수 있음 화학 성분(JIS G4303 / JIS G4311) SUS304의 화학 성분은 일관된 성능을 보장하기 위해 엄격하게 제어됩니다. 원소 함량(%) – 최대/최소 탄소(C) ≤ 0.08 실리콘(Si) ≤ 1.00 망간(Mn) ≤ 2.00 인(P) ≤ 0.045 황(S) ≤ 0.030 크롬(Cr) 18.0 – 20.0 니켈(Ni) 8.0 – 10.5 철(Fe) 밸런스 참고: 모든 값은 JIS G4303-1998 및 JIS G4311-1991 표준을 준수합니다. 기계적 특성(일반 값 – 어닐링 조건) 특성 값 인장 강도 515 – 720 MPa 항복 강도(0.2% 오프셋) ≥ 205 MPa 신도(50 mm) ≥ 40% 경도(HV) 150 – 200 탄성 계수 ~193 GPa 열 전도율 16.2 W/m·K(100°C에서) 계수 열 팽창률 17.2 µm/m·°C(20–100°C) 스프링 적용의 경우 스트립은 종종 1/2 경질(H) 또는 완전 경질(EH/SH) 템퍼로 공급되어 더 높은 항복 강도(최대 1000MPa)와 향상된 탄력성을 제공합니다. 스프링용 정밀 슬릿 SUS304 스트립을 선택하는 이유는 무엇입니까? 스프링에는 영구 변형 없이 반복적인 응력 주기를 견딜 수 있는 재료가 필요합니다. SUS304 스테인레스 스틸 스트립은 다음을 제공합니다. 높은 탄성 한계: 동적 하중 하에서 모양 무결성을 유지합니다. 피로 저항: 고주기 응용 분야(예: 배터리 접점, 릴레이 스프링)에서 안정적으로 작동합니다. 깔끔한 가장자리: 정밀한 슬리팅으로 피로 파괴를 유발할 수 있는 미세 균열과 버를 제거합니다. 부식 방지: 탄소강 스프링과 달리 SUS304는 대부분의 환경에서 도금이나 코팅이 필요하지 않습니다. 생체적합성: 의료용 임플란트 부품에 대한 ISO 10993 표준을 충족합니다(올바르게 마감된 경우). SUS304 스트립으로 만든 일반적인 스프링 유형은 다음과 같습니다. 접촉 스프링(전자 제품) 클립 스프링(자동차 인테리어) 토션 스프링(소형 가전제품) 편평 나선형 스프링(시계, 센서) 제조 및 품질 관리 당사의 SUS304 스트립은 고급 연속 냉간 압연 및 어닐링 라인과 레이저 유도 정밀 슬리팅을 사용하여 생산됩니다. 각 코일은 엄격한 품질 검사를 거칩니다. 치수 정확도: 레이저 마이크로미터 및 광학 에지 스캐너를 통해 확인됩니다. 표면 검사: 자동화된 비전 시스템은 긁힘, 구덩이 또는 롤 자국을 감지합니다. 재료 인증: EN 10204 3.1 또는 3.2에 따라 밀 테스트 보고서(MTR)가 제공됩니다. 배치 추적성: 용융물부터 최종 코일까지 전체 열수 추적. 부가 가치 서비스 옵션: 맞춤형 포장: 수출용 목재 팔레트에 플라스틱 포장 코일. 모서리 조절: 고속 스탬핑을 위한 둥글거나 모따기된 모서리입니다. 무윤활 표면: 클린룸 또는 의료 등급 응용 분야에 적합합니다. 애플리케이션 산업 사용 사례 전자 제품 배터리 접점, SIM 카드 트레이, 스위치 스프링, EMI 차폐 스트립 자동차 안전 벨트 리트랙터, 센서 스프링, 연료 주입기 부품 의료 수술 기구 부품, 이식형 장치 스프링, 진단 장비 산업용 밸브 스프링, 압력 센서, 여과 메쉬 소비재 안경테, 시계 밴드, 주방 기기 경첩 주문 정보 주문하거나 샘플을 요청하려면 다음 세부 정보를 제공하십시오. 등급: SUS304(JIS G4305) 두께: 예: 0.25mm ±0.005mm 너비: 예: 12.5mm ±0.05mm 온도: 어닐링됨 / 1/2H / 스프링 템퍼(스프링용인 경우 지정) 표면 마감: 2B / BA / 맞춤형 코일 ID: 200mm, 300mm 또는 508mm(20") 코일당 무게: 일반적으로 10-50kg(조정 가능) 포장: VCI 종이 + 플라스틱 랩 + 수출 상자 최소 주문 수량(MOQ): 100kg 리드 타임: 7~15일(사양에 따라 다름) 자주 묻는 질문 Q: SUS304는 304 스테인레스 스틸과 동일합니까? A: 예. SUS304는 일본 지정(JIS 표준)이고 304는 AISI/ASTM 지정과 거의 동일합니다. Q: SUS304 스트립을 사용할 수 있습니다. A: SUS304는 대기 부식에 대한 저항력이 우수하지만 장기간 해수에 노출될 경우 SUS316L을 고려하십시오. Q: 2B와 BA 마감의 차이점은 무엇입니까? A: 2B는 반사율이 높으며 매끄럽고 장식용 또는 광학 용도에 이상적입니다. A: 예. RoHS, REACH 및 분쟁 광물 규정을 준수합니다. 결론 정밀 슬릿 모서리가 있는 JIS G4305 SUS304 스테인리스 스틸 스트립(0.1~3.0mm)은 스프링 및 정밀 부품 제조에 있어 탁월한 신뢰성을 제공하며 엄격한 품질 관리, 국제 표준 준수 및 맞춤형 처리가 지원되므로 내구성, 일관성 및 성능을 요구하는 엔지니어가 선택하는 소재입니다. 귀하의 제품은 최고의 기능적 및 미적 표준을 충족합니다. JIS G4305 SUS304 스테인레스 스틸 스트립 두께 0.1 - 3.0mm - 스프링 응용 분야를 위한 정밀 슬릿 커팅 엣지 제품 개요 JIS G4305:2021 표준을 엄격히 준수하여 제조된 SUS304 스테인레스 스틸 스트립은 정밀 엔지니어링 및 산업 응용 분야에서 가장 널리 사용되는 오스테나이트 스테인레스 스틸 등급 중 하나이며 두께 범위는 0.1mm ~ 3.0mm입니다. 이러한 냉간 압연 스트립은 정밀 슬릿 절단 모서리로 특수 처리되어 스프링, 커넥터, 터미널 및 전자 부품과 같은 고성능 부품에 이상적입니다. SUS304(국제적으로 AISI 304 또는 UNS S30400이라고도 함)는 내식성, 성형성, 용접성 및 기계적 강도의 탁월한 균형을 제공하며 일반적으로 18% 크롬과 8% 니켈로 구성되어 주변 환경과 약간 공격적인 환경 모두에서 우수한 성능을 보장합니다. 식품 가공, 의료 기기, 자동차 시스템 및 가전제품을 포함한 이 제품 페이지는 신뢰할 수 있는 내구성이 뛰어난 스테인레스 스틸 스트립 소재를 찾는 엔지니어, 조달 전문가 및 제조업체를 위한 포괄적인 기술 사양, 화학 성분, 기계적 특성 및 적용 지침을 제공합니다. 주요 특징 및 장점 ✅ 규정 준수: JIS G4305:2021(냉간 압연 스테인레스 강판, 시트 및 스트립)을 완벽하게 준수합니다. 자동화된 조립을 위한 마감 ✅ 두께 범위: 0.1mm – 3.0mm(요청 시 맞춤 설정 가능) ✅ 폭 옵션: 5mm – 600mm(표준), 마이크로 스프링 응용 분야에 더 좁은 폭 사용 가능 ✅ 표면 마감: 2B, BA(광택 소둔) 또는 맞춤형 마감(예: 헤어라인, 무광택) ✅ 우수한 스프링 특성: 높은 피로 저항 및 반복 편향 후 탄성 회복 ✅ 부식 저항: 800°C, 습하고 염분 및 약산성 환경에 적합 ✅ 비자성(어닐링 상태): 민감한 전자 및 의료 기기에 이상적 기술 사양 매개변수 사양 표준 JIS G4305:2021 재료 등급 SUS304(일본 산업 표준) 동급 등급 AISI 304(미국), X5CrNi18-10(EN), 1.4301(DIN), 06Cr19Ni10(GB/T) 형태 냉간 압연 스테인레스 스틸 스트립 두께 범위 0.1mm – 3.0mm 폭 범위 5mm – 600mm(±0.05mm 공차의 정밀 슬릿) 공차(두께) ±0.005mm(<0.5mm의 경우), ±1%(≥0.5mm의 경우) 가장자리 상태 정밀 슬릿, 디버링됨, 가장자리 균열 없음 표면 마감 2B(표준), BA(광택 소둔), HL(헤어라인) 또는 고객 지정 열처리 조건 소둔(연질), 1/4H, 1/2H, H, EH, SH(스프링 템퍼 사용 가능) 밀도 7.93 g/cm² 자기 특성 냉간 가공 후 어닐링 상태에서 비자성이 될 수 있음 화학 성분(JIS G4303 / JIS G4311) SUS304는 일관된 성능을 보장하기 위해 엄격하게 제어됩니다. 요소 함량(%) – 최대/최소 탄소(C) ≤ 0.08 실리콘(Si) ≤ 1.00 망간(Mn) ≤ 2.00 인(P) ≤ 0.045 황(S) ≤ 0.030 크롬(Cr) 18.0 – 20.0 니켈(Ni) 8.0 – 10.5 철(Fe) 균형 참고: 모든 값은 JIS G4303-1998 및 JIS G4311-1991 표준을 준수합니다. 기계적 특성(일반 값 – 어닐링 조건) 속성 값 인장 강도 515 – 720 MPa 항복 강도(0.2% 오프셋) ≥ 205 MPa 신장률(50 mm) ≥ 40% 경도(HV) 150 – 200 탄성 계수 ~193 GPa 열 전도성 16.2 W/m·K(100°C에서) 열팽창 계수 17.2 µm/m·°C(20–100°C) 스프링 적용의 경우 스트립은 종종 1/2 하드(H) 또는 완전 하드(EH/SH) 템퍼로 공급되어 더 높은 항복 강도(최대 1000 MPa) 및 향상된 탄력성 스프링용 정밀 슬릿 SUS304 스트립을 선택하는 이유 SUS304 스테인레스 스틸 스트립은 다음을 제공합니다. 높은 탄성 한계: 동적 하중 하에서 형태 무결성 유지: 높은 주기의 응용 분야(예: 배터리 접점, 릴레이 스프링)에서 안정적으로 작동합니다. 정밀 슬릿팅은 피로 파손을 일으킬 수 있는 미세 균열 및 버를 제거합니다. SUS304는 대부분의 환경에서 도금이나 코팅이 필요하지 않습니다. 생체 적합성: 의료용 임플란트 구성 요소에 대한 ISO 10993 표준을 충족합니다(적절하게 마감된 경우) SUS304 스트립으로 만든 일반적인 스프링 유형은 다음과 같습니다. 접촉 스프링(전자 제품) 클립 스프링(자동차 내부) 비틀림 스프링(소형 가전 제품) 편평 나선형 스프링(시계, 센서) 제조 및 품질 관리 당사의 SUS304 스트립은 다음과 같은 고급 연속 냉간 압연 및 어닐링 라인을 사용하여 생산됩니다. 레이저 유도 정밀 슬릿팅을 통해 각 코일은 엄격한 품질 검사를 거칩니다. 치수 정확도: 레이저 마이크로미터 및 광학 엣지 스캐너를 통해 확인됩니다. 표면 검사: 자동화된 비전 시스템이 긁힘, 구멍 또는 롤 자국을 감지합니다. 재료 인증: EN 10204 3.1 또는 3.2에 따라 제공되는 밀 테스트 보고서(MTR): 용융물에서 최종 코일까지 전체 열 수 추적: 맞춤형 포장: 수출용 목재 팔레트의 플라스틱 포장 코일 모서리 컨디셔닝: 고속 스탬핑을 위한 둥근 모서리 또는 모따기된 모서리 무윤활제 표면: 클린룸 또는 의료 등급 응용 분야 산업 사용 사례 전자 제품 배터리 접점, SIM 카드 트레이, 스위치 스프링, EMI 차폐 스트립 자동차 좌석 벨트 견인 장치, 센서 스프링, 연료 주입기 부품 의료 수술 기구 부품, 이식형 장치 스프링, 진단 장비 산업용 밸브 스프링, 압력 센서, 여과 메쉬 안경테, 시계 밴드, 주방 가전 경첩 주문 정보 주문하거나 샘플을 요청하려면 다음 세부 정보를 제공하십시오. 등급: SUS304 (JIS G4305) 두께: 예, 0.25mm ±0.005mm 너비: 예, 12.5mm ±0.05mm 성질: 단련됨 / 1/2H / 스프링 템퍼(스프링용인지 지정) 표면 마감: 2B / BA / Custom 코일 ID: 200mm, 300mm 또는 508mm(20") 코일당 무게: 일반적으로 10~50kg(조정 가능) 포장: VCI 종이 + 플라스틱 랩 + 수출 상자 최소 주문 수량(MOQ): 100kg 리드 타임: 7~15일(사양에 따라 다름) FAQ Q: SUS304는 304 스테인레스 스틸과 동일합니까? 답: 그렇습니다. SUS304는 일본 지정(JIS 표준)이고 304는 AISI/ASTM 지정입니다. 화학적 및 기계적 특성은 거의 동일합니다. Q: SUS304 스트립을 해양 환경에서 사용할 수 있습니까? A: SUS304는 대기 부식에 대한 저항성이 우수하지만 장기간 바닷물에 노출되면 흠집이 생길 수 있습니다. 가혹한 해양 환경에서는 SUS316L을 고려하십시오. Q: 2B와 BA 피니시의 차이점은 무엇인가요? A: 2B는 적당한 반사율을 지닌 표준 밀 마감입니다. BA(Bright Annealed)는 반사율이 높고 매끄러우며 장식 또는 광학 용도에 이상적입니다. Q: RoHS/REACH 준수 문서를 제공합니까? 답: 그렇습니다. 모든 SUS304 스트립은 RoHS, REACH 및 분쟁 광물 규정을 준수합니다. 결론 정밀 슬릿 모서리가 있는 JIS G4305 SUS304 스테인리스 스틸 스트립(0.1~3.0mm)은 스프링 및 정밀 부품 제조에 탁월한 신뢰성을 제공합니다. 엄격한 품질 관리, 국제 표준 준수 및 맞춤형 가공이 뒷받침되는 이 소재는 내구성, 일관성 및 성능을 요구하는 엔지니어가 선택하는 소재입니다. 마이크로 전자 접점을 설계하든 자동차 안전 메커니즘을 설계하든 당사의 SUS304 스트립은 귀하의 제품이 최고의 기능적 및 미적 표준을 충족하도록 보장합니다.
식품 및 의료용 고정밀 316L/1.4404/SUS316L 스테인레스 스틸 스트립(0.1mm – 3.0mm)
소개
까다로운 식품 가공 및 의료 기기 제조 부문에서 재료 무결성, 내부식성 및 생체 적합성은 협상할 수 없습니다. 이러한 엄격한 요구 사항을 충족하는 가장 신뢰할 수 있는 재료는 다음과 같습니다.316L 스테인레스 스틸, 국제적으로 알려진1.4404(유럽 표준 EN 10088)그리고SUS316L(일본공업규격 JIS G4303). 이 합금으로 제작된 고정밀 스테인레스 스틸 스트립 - 두께는0.1mm ~ 3.0mm—위생적이고 멸균되었으며 화학적으로 공격적인 환경에서 탁월한 성능을 제공하도록 설계되었습니다. 이 기사에서는 비교 데이터 표를 통해 지원되는 고정밀 316L 스테인레스 스틸 스트립의 구성, 특성, 제조 표준, 적용 및 장점을 살펴봅니다.
재료 개요: 316L / 1.4404 / SUS316L
316L은 316 오스테나이트 스테인리스강 제품군의 저탄소 변형입니다. "L"은 최대 탄소 함량을 나타냅니다.0.03%이는 다음과 같은 위험을 크게 줄여줍니다.감작(크롬 탄화물 석출)은 용접 또는 고온 노출 중 발생하므로 중요한 응용 분야의 용접 부품에 이상적입니다.
지역적으로 약간의 명칭 차이가 있음에도 불구하고,316L(ASTM/UNS), 1.4404(EN) 및 SUS316L(JIS)화학적 조성과 기계적 거동이 본질적으로 동일합니다. 세 가지 표준 모두 우수한 내식성과 성형성을 보장하기 위해 황, 인과 같은 불순물에 대한 엄격한 제한을 지정합니다.
화학 성분(일반, 중량%)
| 요소 |
316L(ASTM A240) |
1.4404(EN 10088-2) |
SUS316L(JIS G4303) |
| 탄소(C) |
≤ 0.03 |
≤ 0.03 |
≤ 0.03 |
| 크롬(Cr) |
16.0~18.0 |
16.5~18.5 |
16.0~18.0 |
| 니켈(Ni) |
10.0~14.0 |
10.0~13.0 |
10.0~14.0 |
| 몰리브덴(Mo) |
2.0~3.0 |
2.0–2.5 |
2.0~3.0 |
| 망간(Mn) |
≤ 2.0 |
≤ 2.0 |
≤ 2.0 |
| 실리콘(Si) |
≤ 0.75 |
≤ 1.0 |
≤ 1.0 |
| 인(P) |
≤ 0.045 |
≤ 0.045 |
≤ 0.045 |
| 유황(S) |
≤ 0.03 |
≤ 0.015 |
≤ 0.03 |
| 철(Fe) |
균형 |
균형 |
균형 |
참고: 지역 표준으로 인해 약간의 차이가 있지만 기능적 성능은 일관되게 유지됩니다.
추가몰리브덴(2~3%)316L과 304 스테인리스강의 주요 차이점입니다. 몰리브덴은 다음에 대한 저항성을 획기적으로 향상시킵니다.구멍 및 틈새 부식특히 해수, 식염수 또는 식품 공장에서 사용되는 세척제와 같이 염화물이 풍부한 환경에서 그렇습니다.
식품 및 의료용 주요 특성
고정밀 316L 스트립은 규제 산업에 필수적인 물리적, 기계적 및 표면 특성의 고유한 조합을 나타냅니다.
- 부식 저항: 식품 가공 및 살균 시 발생하는 유기산(예: 구연산, 젖산), 무기산(예: 질산) 및 염 용액에 대한 저항력이 있습니다.
- 생체적합성: 의료용 임플란트 및 기기에 대한 ISO 10993 및 USP Class VI 표준을 준수합니다.
- 위생적인 표면 마감: 다음과 같은 마감재로 사용 가능BA(광택 소둔), 2B 또는 맞춤형 전해연마 표면박테리아 부착을 방지하기 위해 Ra < 0.2 µm를 사용합니다.
- 비자성(어닐링 상태): MRI 호환 의료기기에 필수입니다.
- 우수한 성형성 및 용접성: 균열이나 내식성 손실 없이 복잡한 스탬핑, 벤딩, 레이저 용접이 가능합니다.
- 열 안정성: 최대 870°C의 극저온에서도 무결성을 유지합니다(간헐적 서비스).
치수 정밀도 및 공차
수술용 블레이드, 미세유체 채널 또는 센서 다이어프램과 같이 미크론 수준의 정확도가 필요한 응용 분야의 경우 스트립 두께 공차가 가장 중요합니다. 고정밀 냉간 압연 316L 스트립은 엄격한 공정 제어 하에 제조되며 종종 ASTM A480 또는 EN 10258 표준을 초과합니다.
일반적인 두께 공차(냉간 압연, 어닐링 및 산세)
| 호칭두께(mm) |
표준 공차(±mm) |
고정밀 공차(±mm) |
| 0.10 |
±0.010 |
±0.005 |
| 0.20 |
±0.012 |
±0.006 |
| 0.50 |
±0.020 |
±0.010 |
| 1.00 |
±0.030 |
±0.015 |
| 2.00 |
±0.040 |
±0.020 |
| 3.00 |
±0.050 |
±0.025 |
다중 패스 롤링, 장력 레벨링 및 레이저 마이크로미터 모니터링을 통해 고정밀 공차를 달성할 수 있습니다.
너비는 일반적으로 다음과 같습니다.5mm ~ 650mm, 다음과 같은 가장자리 조건이 있습니다.슬릿 가장자리(SE), 둥근 가장자리(RE) 또는 디버링된 가장자리(DE)미세한 찢어짐이나 오염을 방지합니다.
제조공정
고정밀 316L 스트립을 생산하려면 다음과 같은 몇 가지 중요한 단계가 필요합니다.
- 용해 및 주조: 진공유도용해(VIM) 또는 AOD(아르곤산소 탈탄) 방식으로 초저탄소 및 최소한의 함유물을 보장합니다.
- 열간압연: 슬래브를 가열하여 코일(두께 ~3~6mm)로 만듭니다.
- 냉간 압연: 여러 번의 패스를 통해 두께를 최종 치수로 감소시키는 동시에 표면 조도 및 기계적 강도를 향상시킵니다.
- 가열 냉각: 수소-질소 분위기에서 광휘소둔하여 산화를 방지하고 연성을 회복시킵니다.
- 산세/전해연마: 스케일을 제거하고 부동태 크롬산화층을 강화합니다.
- 슬리팅 및 검사: 고객의 폭에 맞춰 정밀하게 절단합니다. CCD 카메라를 통한 100% 표면 검사.
품질 보증에는 다음이 포함됩니다.분광 분석, 인장 테스트, 입계 부식 테스트(예: ASTM A262 Practice E) 및 표면 거칠기 측정.
식품 산업의 응용
316L 스테인레스 스틸 스트립은 산성 식품(토마토 소스, 식초), 알칼리성 세제(NaOH)에 대한 저항성 및 저온살균 중 열 순환으로 인해 식품 기계에 없어서는 안 될 요소입니다.
일반적인 용도:
- 컨베이어 벨트 및 가이드 레일
- 절단 블레이드 및 슬라이서 구성 요소
- 충전 기계용 씰 및 개스킷
- 유제품 저온살균기의 열교환기 핀
- 양조 및 와인 제조 장비의 구성 요소
규정 준수FDA 21 CFR 178.3297,EC 1935/2004, 그리고3-A 위생 기준정기적으로 확인됩니다.
의료 부문의 응용
의료 기술에서 316L의 생체 적합성과 살균성은 일회용 장치와 이식형 장치 모두에 적합합니다.
주요 응용 분야:
- 수술기구 구성품(가위, 겸자)
- 정형외과 임플란트 블랭크(뼈 나사, 플레이트)
- 카테터 가이드와이어 및 스텐트 전구체
- 진단 센서 멤브레인
- 치과 도구 및 교정용 와이어
전해연마된 316L 스트립은 표면 결함을 줄이고 혈전을 최소화하며 피로 수명을 향상시킵니다. 이는 심혈관 장치에 매우 중요합니다.
대안에 비해 장점
| 재료 |
부식 저항 |
생체적합성 |
비용 |
자기? |
일반적인 제한사항 |
| 316L SS |
훌륭한 |
높은 |
중간 |
아니요* |
CoCr 합금에 비해 낮은 강도 |
| 304 SS |
좋음(Cl⁻에서는 나쁨) |
보통의 |
낮은 |
아니요* |
식염수에 움푹 패이는 경향이 있음 |
| 티타늄 등급 2 |
훌륭한 |
훌륭한 |
높은 |
아니요 |
기계/성형이 어려움 |
| CoCr 합금 |
훌륭한 |
훌륭한 |
매우 높음 |
약간 |
깨지기 쉽고 비싸다 |
| 알류미늄 |
가난한 |
낮은 |
낮은 |
아니요 |
습한/산성 환경에는 적합하지 않습니다. |
*어닐링 상태에서는 비자성입니다. 냉간 가공 후에는 약간 자성이 생길 수 있습니다.
316L은 다음과 같은 최적의 균형을 유지합니다.성능, 제조 가능성 및 비용 효율성중급 및 고급 의료 및 식품 응용 분야에 적합합니다.
품질 인증 및 추적성
평판이 좋은 공급업체는 다음을 제공합니다.
- EN 10204 3.1 또는 3.2에 따른 밀 테스트 보고서(MTR)
- 전체 화학 및 기계 테스트 데이터
- 배치 추적성(열수 추적)
- 인증: ISO 13485(의료), ISO 22000(식품 안전), ASME BPE
이를 통해 글로벌 규제 프레임워크를 완벽하게 준수하고 감사를 용이하게 합니다.
결론
고정밀 316L / 1.4404 / SUS316L 스테인리스 스틸 스트립(0.1~3.0mm)은 가장 위생적이고 부식성이 있는 환경에서 작동하는 구성품의 표준을 나타냅니다. 몰리브덴으로 강화된 뛰어난 내식성과 생체 적합성, 치수 정확도 및 표면 품질이 결합되어 식품 가공 장비 및 생명을 구하는 의료 기기에서 대체할 수 없는 제품이 되었습니다. 업계가 계속해서 더 깨끗하고 안전하며 신뢰할 수 있는 재료를 요구함에 따라 316L 스테인레스 스틸 스트립은 고급 엔지니어링 솔루션의 최전선에 남을 것입니다.




 라이안 이오네스쿠매우 좋은 소재 품질. 우리는 10년 이상을 협력하게 합니다. 그들은 강철 소재의 다량 종류를 거래합니다. 좋은 모든 소재 품질. 그들 모든 소재 품질을 위한 의무. 우리는 활공하고 있고 계속되고 미래에 그들과 협력합니다
라이안 이오네스쿠매우 좋은 소재 품질. 우리는 10년 이상을 협력하게 합니다. 그들은 강철 소재의 다량 종류를 거래합니다. 좋은 모든 소재 품질. 그들 모든 소재 품질을 위한 의무. 우리는 활공하고 있고 계속되고 미래에 그들과 협력합니다![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()