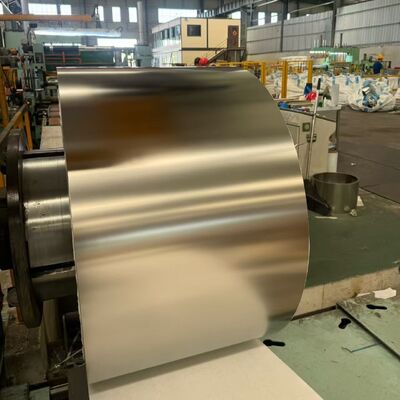
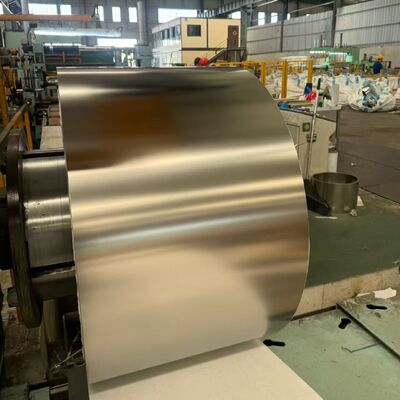
Bandes d'acier inoxydable de haute précision 316L/1,4404/SUS316L 0,1 mm - 3,0 mm pour le secteur alimentaire et médical
Spécification des produits
| Produits |
bande d'acier inoxydable |
| Épaisseur |
0,1-3,0 mm |
| Largeur |
largeur minimale 5 mm |
| Quantité minimale de commande |
20 kg |
| Catégorie principale |
201 301 304 304L 309S 310S 316L 316Ti 410 420 430 436 439 441 444 440A/B/C,2205,2507,904L,C276,400,600,625,926,825.etc |
| Surface |
BA2B |
| Standard |
ASTM EN GB JIS |
| Emballage |
cadre en bois et papier imperméable |
Bandes d'acier inoxydable JIS G4305 SUS304 d'épaisseur 0,1 à 3,0 mm – Bord de coupe fendu de précision pour les applications à ressorts Présentation du produit Les bandes d'acier inoxydable SUS304, fabriquées en stricte conformité avec la norme JIS G4305 : 2021, représentent l'une des nuances d'acier inoxydable austénitique les plus largement utilisées dans l'ingénierie de précision et les applications industrielles. Avec une plage d'épaisseur de 0,1 mm à 3,0 mm, ces bandes laminées à froid sont spécialement traitées avec des bords coupants fendus de précision, ce qui les rend idéales pour les composants hautes performances tels que les ressorts, les connecteurs, les bornes et les pièces électroniques. Le SUS304 (également connu internationalement sous le nom d'AISI 304 ou UNS S30400) offre un excellent équilibre entre résistance à la corrosion, formabilité, soudabilité et résistance mécanique. Sa composition (généralement 18 % de chrome et 8 % de nickel) garantit des performances supérieures dans les environnements ambiants et légèrement agressifs, notamment dans la transformation des aliments, les dispositifs médicaux, les systèmes automobiles et l'électronique grand public. Cette page produit fournit des spécifications techniques complètes, la composition chimique, les propriétés mécaniques et des conseils d'application pour les ingénieurs, les spécialistes des achats et les fabricants à la recherche de matériaux de bandes d'acier inoxydable fiables et à haute tolérance. Principales caractéristiques et avantages ✅ Conformité : entièrement conforme à la norme JIS G4305:2021 (plaques, feuilles et bandes en acier inoxydable laminées à froid) ✅ Fendage de précision : tolérance des bords ± 0,01 mm ; finition sans bavure pour un assemblage automatisé ✅ Plage d'épaisseur : 0,1 mm – 3,0 mm (personnalisable sur demande) ✅ Options de largeur : 5 mm – 600 mm (standard) ; largeurs plus étroites disponibles pour les applications de micro-ressorts ✅ Finition de surface : 2B, BA (Bright Recuit) ou finitions personnalisées (par exemple, délié, mat) ✅ Excellentes propriétés de ressort : Haute résistance à la fatigue et récupération élastique après des déformations répétées ✅ Résistance à la corrosion : Résiste à l'oxydation jusqu'à 800°C ; convient aux environnements humides, salins et légèrement acides ✅ Non magnétique (état recuit) : idéal pour les instruments électroniques et médicaux sensibles Spécifications techniques Paramètre Spécification Norme JIS G4305:2021 Qualité du matériau SUS304 (norme industrielle japonaise) Qualités équivalentes AISI 304 (USA), X5CrNi18-10 (EN), 1.4301 (DIN), 06Cr19Ni10 (GB/T) Forme Bande d'acier inoxydable laminée à froid Plage d'épaisseur 0,1 mm – 3,0 mm Plage de largeur 5 mm – 600 mm (fente de précision jusqu'à une tolérance de ±0,05 mm) Tolérance (épaisseur) ±0,005 mm (pour <0,5 mm) ; ±1 % (pour ≥0,5 mm) État des bords Fente de précision, ébavuré, pas de fissures des bords État de surface 2B (standard), BA (recuit brillant), HL (délié) ou état de trempe spécifié par le client Recuit (doux), 1/4H, 1/2H, H, EH, SH (trempe à ressort disponible) Densité 7,93 g/cm³ Propriété magnétique Non magnétique à l'état recuit ; peut devenir légèrement magnétique après travail à froid Composition chimique (JIS G4303 / JIS G4311) La composition chimique du SUS304 est étroitement contrôlée pour garantir des performances constantes : Teneur en éléments (%) – Max/Min Carbone (C) ≤ 0,08 Silicium (Si) ≤ 1,00 Manganèse (Mn) ≤ 2,00 Phosphore (P) ≤ 0,045 Soufre (S) ≤ 0,030 Chrome (Cr) 18,0 – 20,0 Nickel (Ni) 8,0 – 10,5 Fer (Fe) Balance Remarque : Toutes les valeurs sont conformes aux normes JIS G4303-1998 et JIS G4311-1991. Propriétés mécaniques (valeurs typiques – état recuit) Valeur de propriété Résistance à la traction 515 – 720 MPa Limite d'élasticité (décalage de 0,2 %) ≥ 205 MPa Allongement (en 50 mm) ≥ 40 % Dureté (HV) 150 – 200 Module d'élasticité ~ 193 GPa Conductivité thermique 16,2 W/m·K (à 100°C) Coefficient de dilatation thermique 17,2 µm/m·°C (20-100°C) Pour les applications à ressorts, les bandes sont souvent fournies dans des états 1/2 dur (H) ou entièrement dur (EH/SH), offrant une limite d'élasticité plus élevée (jusqu'à 1 000 MPa) et une résilience améliorée. Pourquoi choisir des bandes SUS304 fendues avec précision pour les ressorts ? Les ressorts nécessitent des matériaux capables de supporter des cycles de contraintes répétés sans déformation permanente. Les bandes en acier inoxydable SUS304 offrent : Limite d'élasticité élevée : maintient l'intégrité de la forme sous charge dynamique. Résistance à la fatigue : fonctionne de manière fiable dans les applications à cycles élevés (par exemple, contacts de batterie, ressorts de relais). Bords propres : la fente de précision élimine les microfissures et les bavures qui pourraient provoquer une rupture par fatigue. Protection contre la corrosion : contrairement aux ressorts en acier au carbone, le SUS304 ne nécessite pas de placage ou de revêtement dans la plupart des environnements. Biocompatibilité : Conforme aux normes ISO 10993 pour les composants d'implants médicaux (lorsqu'ils sont correctement finis). Les types de ressorts courants fabriqués à partir de bandes SUS304 comprennent : Ressorts de contact (électronique) Ressorts à clip (intérieurs automobiles) Ressorts de torsion (petits appareils électroménagers) Ressorts hélicoïdaux plats (montres, capteurs) Fabrication et contrôle qualité Nos bandes SUS304 sont produites à l'aide de lignes avancées de laminage à froid et de recuit continus, suivies d'une refente de précision guidée par laser. Chaque bobine est soumise à des contrôles de qualité rigoureux : Précision dimensionnelle : vérifiée via des micromètres laser et des scanners de bords optiques. Inspection des surfaces : les systèmes de vision automatisés détectent les rayures, les piqûres ou les marques de roulement. Certification des matériaux : rapports de tests d'usine (MTR) fournis conformément à la norme EN 10204 3.1 ou 3.2. Traçabilité des lots : suivi complet du numéro de chaleur, de la fusion à la bobine finale. Services optionnels à valeur ajoutée : Emballage personnalisé : bobines enveloppées de plastique sur des palettes en bois pour l'exportation. Conditionnement des bords : bords arrondis ou chanfreinés pour un estampage à grande vitesse. Surface sans lubrifiant : Pour les applications en salle blanche ou de qualité médicale. Applications Cas d'utilisation dans l'industrie Électronique Contacts de batterie, plateaux de carte SIM, ressorts de commutation, bandes de blindage EMI Automobile Rétracteurs de ceinture de sécurité, ressorts de capteur, composants d'injecteur de carburant Médical Pièces d'instruments chirurgicaux, ressorts de dispositif implantable, équipement de diagnostic Ressorts de valve industriels, capteurs de pression, maille de filtration Biens de consommation Montures de lunettes, bracelets de montre, charnières d'appareils de cuisine Informations de commande Pour passer une commande ou demander un échantillon, veuillez fournir les détails suivants : Grade : SUS304 (JIS G4305) Épaisseur : par exemple, 0,25 mm ±0,005 mm Largeur : par exemple, 12,5 mm ±0,05 mm État : recuit / 1/2H / revenu à ressort (préciser si pour une utilisation à ressort) Finition de surface : 2B / BA / ID de bobine personnalisé : 200 mm, 300 mm ou 508 mm (20") Poids par bobine : généralement 10 à 50 kg (réglable) Emballage : papier VCI + plastique emballage + caisse d'exportation Quantité minimum de commande (MOQ) : 100 kg Délai de livraison : 7 à 15 jours (selon les spécifications) FAQ Q : Le SUS304 est-il le même que l'acier inoxydable 304 ? R : Oui, SUS304 est la désignation japonaise (norme JIS), tandis que 304 est la désignation AISI/ASTM. Les propriétés chimiques et mécaniques sont presque identiques. offre une bonne résistance à la corrosion atmosphérique mais peut se piquer en cas d'exposition prolongée à l'eau de mer. Pour une utilisation marine difficile, pensez au SUS316L. Q : Quelle est la différence entre la finition 2B et BA ? Conclusion Les bandes en acier inoxydable JIS G4305 SUS304 (0,1 à 3,0 mm) avec des bords fendus de précision offrent une fiabilité inégalée pour la fabrication de ressorts et de composants de précision. Soutenues par un contrôle de qualité rigoureux, une conformité aux normes internationales et un traitement personnalisable, elles sont le matériau de choix pour les ingénieurs exigeant durabilité, cohérence et performances. normes.JIS G4305 SUS304 Bandes d'acier inoxydable d'épaisseur 0,1 - 3,0 mm - Tranchant fendu de précision pour les applications de ressorts Présentation du produit Les bandes d'acier inoxydable SUS304, fabriquées en stricte conformité avec la norme JIS G4305 : 2021, représentent l'une des nuances d'acier inoxydable austénitique les plus largement utilisées dans l'ingénierie de précision et les applications industrielles. Avec une plage d'épaisseur de 0,1 mm à 3,0 mm, ces bandes laminées à froid sont. spécialement traité avec des bords tranchants fendus de précision, ce qui les rend idéaux pour les composants hautes performances tels que les ressorts, les connecteurs, les bornes et les pièces électroniques. Le SUS304 (également connu internationalement sous le nom d'AISI 304 ou UNS S30400) offre un excellent équilibre entre résistance à la corrosion, formabilité, soudabilité et résistance mécanique. Sa composition (généralement 18 % de chrome et 8 % de nickel) garantit des performances supérieures dans les environnements ambiants et légèrement agressifs, y compris la transformation des aliments, les dispositifs médicaux et l'automobile. systèmes et appareils électroniques grand public. Cette page produit fournit des spécifications techniques complètes, une composition chimique, des propriétés mécaniques et des conseils d'application pour les ingénieurs, les spécialistes des achats et les fabricants à la recherche de matériaux de bandes d'acier inoxydable fiables et à haute tolérance. Caractéristiques et avantages clés ✅ Conformité : entièrement conforme à la norme JIS G4305:2021 (plaques, feuilles et bandes en acier inoxydable laminées à froid) ✅ Fendage de précision : tolérance des bords ± 0,01 mm ; ✅ Plage d'épaisseur : 0,1 mm – 3,0 mm (personnalisable sur demande) ✅ Options de largeur : 5 mm – 600 mm (standard) ; largeurs plus étroites disponibles pour les applications de micro-ressorts ✅ Finition de surface : 2B, BA (recuit brillant) ou finitions personnalisées (par exemple, délié, mat) ✅ Excellentes propriétés du ressort : haute résistance à la fatigue et récupération élastique après des déformations répétées ✅ Résistance à la corrosion : résiste à l'oxydation jusqu'à 800 °C ; convient aux environnements humides, salins et légèrement acides ✅ Non magnétique (état recuit) : idéal pour les instruments électroniques et médicaux sensibles Spécifications techniques Paramètre Spécification Norme JIS G4305 : 2021 Qualité du matériau SUS304 (norme industrielle japonaise) Qualités équivalentes AISI 304 (USA), X5CrNi18-10 (EN), 1.4301 (DIN), 06Cr19Ni10 (GB/T) Forme Bande d'acier inoxydable laminée à froid Plage d'épaisseur 0,1 mm – 3,0 mm Plage de largeur 5 mm – 600 mm (fente de précision jusqu'à une tolérance de ± 0,05 mm) Tolérance (épaisseur) ± 0,005 mm (pour < ± 1 % (pour ≥ 0,5 mm) État du bord Fente de précision, ébavurée, pas de fissures de bord Finition de surface) ; 2B (standard), BA (recuit brillant), HL (délié) ou état de trempe spécifié par le client Recuit (doux), 1/4H, 1/2H, H, EH, SH (trempe à ressort disponible) Densité 7,93 g/cm³ Propriété magnétique Non magnétique à l'état recuit peut devenir légèrement magnétique après un travail à froid Composition chimique (JIS G4303 / JIS G4311) La composition chimique du SUS304 ; est étroitement contrôlé pour garantir des performances constantes : Teneur en éléments (%) – Max/Min Carbone (C) ≤ 0,08 Silicium (Si) ≤ 1,00 Manganèse (Mn) ≤ 2,00 Phosphore (P) ≤ 0,045 Soufre (S) ≤ 0,030 Chrome (Cr) 18,0 – 20,0 Nickel (Ni) 8,0 – 10,5 Balance en fer (Fe) Remarque : Toutes les valeurs sont conformes aux normes JIS G4303-1998 et JIS G4311-1991. Propriétés mécaniques (valeurs typiques – état recuit) Valeur de la propriété Résistance à la traction 515 – 720 MPa Limite d'élasticité (décalage de 0,2 %) ≥ 205 MPa Allongement (en 50 mm) ≥ 40 % Dureté. (HV) 150 – 200 Module d'élasticité ~193 GPa Conductivité thermique 16,2 W/m·K (à 100°C) Coefficient de dilatation thermique 17,2 µm/m·°C (20–100°C) Pour les applications à ressorts, les bandes sont souvent fournies dans des états 1/2 dur (H) ou entièrement dur (EH/SH), offrant une limite d'élasticité plus élevée (jusqu'à 1 000 MPa) et une résilience améliorée. Pourquoi choisir les bandes SUS304 à fente de précision pour les ressorts ? Les ressorts nécessitent des matériaux capables de supporter des cycles de contraintes répétés sans déformation permanente. Les bandes en acier inoxydable SUS304 offrent : Limite d'élasticité élevée : maintient l'intégrité de la forme sous charge dynamique. Résistance à la fatigue : fonctionne de manière fiable dans les applications à cycles élevés (par exemple, les contacts de batterie, les ressorts de relais). ressorts en acier, SUS304 ne nécessite pas de placage ou de revêtement dans la plupart des environnements. Biocompatibilité : répond aux normes ISO 10993 pour les composants d'implants médicaux (lorsqu'ils sont correctement finis). Les types de ressorts courants fabriqués à partir de bandes SUS304 comprennent : Ressorts de contact (électronique) Ressorts à pince (intérieurs automobiles) Ressorts de torsion (petits appareils électroménagers) Ressorts hélicoïdaux plats (montres, capteurs) Fabrication et contrôle qualité Nos bandes SUS304 sont produites à l'aide d'un laminage à froid et d'un recuit continus avancés. lignes, suivies d'une refente de précision guidée par laser. Chaque bobine est soumise à des contrôles de qualité rigoureux : Précision dimensionnelle : vérifiée via des micromètres laser et des scanners de bords optiques. Inspection de surface : les systèmes de vision automatisés détectent les rayures, les piqûres ou les marques de rouleau. Certification des matériaux : Rapports de test d'usine (MTR) fournis selon la norme EN 10204 3.1 ou 3.2. Traçabilité des lots : suivi complet du nombre de chaleur de la fusion à la bobine finale. Bobines enveloppées de plastique sur des palettes en bois pour l'exportation. Conditionnement des bords : bords arrondis ou chanfreinés pour un estampage à grande vitesse. Surface sans lubrifiant : pour les applications en salle blanche ou de qualité médicale. Applications Cas d'utilisation dans l'industrie Électronique Contacts de batterie, plateaux de carte SIM, ressorts de commutateur, bandes de blindage EMI Rétracteurs de ceinture de sécurité automobile, ressorts de capteur, composants d'injecteur de carburant Pièces d'instruments chirurgicaux médicaux, ressorts de dispositifs implantables, équipements de diagnostic Ressorts de valve industriels, capteurs de pression, maille de filtration Biens de consommation Lunettes cadres, bracelets de montre, charnières d'appareils de cuisine Informations de commande Pour passer une commande ou demander un échantillon, veuillez fournir les détails suivants : Grade : SUS304 (JIS G4305) Épaisseur : par exemple, 0,25 mm ±0,005 mm Largeur : par exemple, 12,5 mm ±0,05 mm État : recuit / 1/2H / revenu à ressort (préciser si pour une utilisation à ressort) Finition de surface : 2B / BA / ID de bobine personnalisé : 200 mm, 300 mm ou 508 mm (20") Poids par bobine : généralement 10 à 50 kg (réglable) Emballage : papier VCI + film plastique + caisse d'exportation Quantité minimale de commande (MOQ) : 100 kg Délai de livraison : 7 à 15 jours (selon les spécifications) FAQ Q : Le SUS304 est-il le même que l'acier inoxydable 304 ? R : Oui. SUS304 est la désignation japonaise (norme JIS), tandis que 304 est la désignation AISI/ASTM. Les propriétés chimiques et mécaniques sont presque identiques. Q : Les bandes SUS304 peuvent-elles être utilisées dans les environnements marins ? R : Le SUS304 offre une bonne résistance à la corrosion atmosphérique mais peut se piquer en cas d'exposition prolongée à l'eau de mer. Pour une utilisation marine intensive, pensez au SUS316L. Q : Quelle est la différence entre les finitions 2B et BA ? R : 2B est une finition standard avec une réflectivité modérée. BA (Bright Annealed) est hautement réfléchissant, lisse et idéal pour les applications décoratives ou optiques. Q : Fournissez-vous une documentation de conformité RoHS/REACH ? R : Oui. Toutes nos bandes SUS304 sont conformes aux réglementations RoHS, REACH et sur les minéraux de conflit. Conclusion Les bandes en acier inoxydable JIS G4305 SUS304 (0,1 à 3,0 mm) avec bords fendus de précision offrent une fiabilité inégalée pour la fabrication de ressorts et de composants de précision. Soutenus par un contrôle de qualité rigoureux, une conformité aux normes internationales et un traitement personnalisable, ils constituent le matériau de choix pour les ingénieurs exigeant durabilité, cohérence et performances. Que vous conceviez des contacts microélectroniques ou des mécanismes de sécurité automobile, nos bandes SUS304 garantissent que vos produits répondent aux normes fonctionnelles et esthétiques les plus élevées.
Bandes en acier inoxydable 316L/1.4404/SUS316L de haute précision (0,1 mm – 3,0 mm) pour applications alimentaires et médicales
Introduction
Dans les secteurs exigeants de la transformation des aliments et de la fabrication de dispositifs médicaux, l’intégrité des matériaux, la résistance à la corrosion et la biocompatibilité ne sont pas négociables. Parmi les matériaux les plus fiables répondant à ces exigences strictes figurentAcier inoxydable 316L, connu internationalement sous le nom1.4404 (norme européenne EN 10088)etSUS316L (norme industrielle japonaise JIS G4303). Bandes d'acier inoxydable de haute précision fabriquées à partir de cet alliage, d'une épaisseur allant de0,1 mm à 3,0 mm— sont conçus pour offrir des performances exceptionnelles dans des environnements hygiéniques, stériles et chimiquement agressifs. Cet article explore la composition, les propriétés, les normes de fabrication, les applications et les avantages des bandes d'acier inoxydable 316L de haute précision, étayés par des tableaux de données comparatifs.
Aperçu des matériaux : 316L / 1.4404 / SUS316L
Le 316L est une variante à faible teneur en carbone de la famille des aciers inoxydables austénitiques 316. Le « L » désigne une teneur maximale en carbone de0,03%, ce qui réduit considérablement le risque desensibilisation(précipitation de carbure de chrome) pendant le soudage ou l'exposition à des températures élevées, ce qui le rend idéal pour les composants soudés dans les applications critiques.
Malgré des différences de dénomination régionales mineures,316L (ASTM/UNS), 1.4404 (EN) et SUS316L (JIS)sont essentiellement équivalents en termes de composition chimique et de comportement mécanique. Les trois normes spécifient des limites strictes sur les impuretés comme le soufre et le phosphore pour garantir une résistance à la corrosion et une formabilité supérieures.
Composition chimique (typique, % en poids)
| Élément |
316L (ASTM A240) |
1.4404 (EN 10088-2) |
SUS316L (JIS G4303) |
| Carbone (C) |
≤ 0,03 |
≤ 0,03 |
≤ 0,03 |
| Chrome (Cr) |
16,0-18,0 |
16,5-18,5 |
16,0-18,0 |
| Nickel (Ni) |
10,0 à 14,0 |
10,0-13,0 |
10,0 à 14,0 |
| Molybdène (Mo) |
2,0-3,0 |
2,0-2,5 |
2,0-3,0 |
| Manganèse (Mn) |
≤ 2,0 |
≤ 2,0 |
≤ 2,0 |
| Silicium (Si) |
≤ 0,75 |
≤ 1,0 |
≤ 1,0 |
| Phosphore (P) |
≤ 0,045 |
≤ 0,045 |
≤ 0,045 |
| Soufre (S) |
≤ 0,03 |
≤ 0,015 |
≤ 0,03 |
| Fer (Fe) |
Équilibre |
Équilibre |
Équilibre |
Remarque : Des variations mineures existent en raison des normes régionales, mais les performances fonctionnelles restent cohérentes.
L'ajout demolybdène (2 à 3 %)est le différenciateur clé entre l’acier inoxydable 316L et l’acier inoxydable 304. Le molybdène améliore considérablement la résistance àcorrosion par piqûres et fissures, en particulier dans les environnements riches en chlorures, tels que l'eau de mer, les solutions salines ou les agents de nettoyage utilisés dans les usines alimentaires.
Propriétés clés pour un usage alimentaire et médical
Les bandes 316L de haute précision présentent une combinaison unique de caractéristiques physiques, mécaniques et de surface essentielles pour les industries réglementées :
- Résistance à la corrosion: Résiste aux acides organiques (par exemple citrique, lactique), aux acides inorganiques (par exemple nitrique) et aux solutions salines rencontrées dans la transformation des aliments et la stérilisation.
- Biocompatibilité: Conforme aux normes ISO 10993 et USP Classe VI pour les implants et dispositifs médicaux.
- Finition de surface hygiénique: Disponible dans des finitions telles queBA (Bright Annealed), 2B ou surfaces électropolies personnaliséesavec Ra < 0,2 µm pour empêcher l’adhésion bactérienne.
- Non magnétique (en état recuit): Critique pour les instruments médicaux compatibles IRM.
- Excellente formabilité et soudabilité: Permet un emboutissage, un pliage et un soudage laser complexes sans fissuration ni perte de résistance à la corrosion.
- Stabilité thermique: Maintient l'intégrité des températures cryogéniques jusqu'à 870°C (service intermittent).
Précision dimensionnelle et tolérances
Pour les applications nécessitant une précision au micron, telles que les lames chirurgicales, les canaux microfluidiques ou les diaphragmes de capteurs, la tolérance sur l'épaisseur de la bande est primordiale. Les bandes 316L laminées à froid de haute précision sont fabriquées sous un contrôle de processus strict, dépassant souvent les normes ASTM A480 ou EN 10258.
Tolérances d'épaisseur typiques (laminées à froid, recuites et décapées)
| Épaisseur nominale (mm) |
Tolérance standard (± mm) |
Tolérance de haute précision (± mm) |
| 0,10 |
±0,010 |
±0,005 |
| 0,20 |
±0,012 |
±0,006 |
| 0,50 |
±0,020 |
±0,010 |
| 1h00 |
±0,030 |
±0,015 |
| 2h00 |
±0,040 |
±0,020 |
| 3h00 |
±0,050 |
±0,025 |
Des tolérances de haute précision sont possibles grâce au laminage multi-passes, au nivellement de tension et à la surveillance micrométrique laser.
Les largeurs varient généralement de5 mm à 650 mm, avec des conditions de bord incluantbord fendu (SE), bord arrondi (RE) ou bord ébavuré (DE)pour éviter les micro-déchirures ou la contamination.
Processus de fabrication
La production de bandes 316L de haute précision implique plusieurs étapes critiques :
- Fusion et coulée: La fusion par induction sous vide (VIM) ou AOD (Argon Oxygen Decarburization) garantit une teneur en carbone ultra faible et des inclusions minimales.
- Laminage à chaud: Les dalles sont chauffées et roulées en bobines (~ 3 à 6 mm d'épaisseur).
- Laminage à froid: Les passes multiples réduisent l'épaisseur aux dimensions finales tout en améliorant l'état de surface et la résistance mécanique.
- Recuit: Le recuit brillant sous atmosphère hydrogène-azote empêche l’oxydation et restaure la ductilité.
- Décapage/Électropolissage: Élimine le tartre et améliore la couche passive d'oxyde de chrome.
- Défendage et inspection: Refendage de précision aux largeurs du client ; Inspection 100% des surfaces via caméras CCD.
L'assurance qualité comprendanalyse spectrométrique, essais de traction, essais de corrosion intergranulaire (par exemple, ASTM A262 Practice E) et mesure de la rugosité de surface.
Applications dans l'industrie alimentaire
Les bandes en acier inoxydable 316L sont indispensables dans les machines alimentaires en raison de leur résistance aux aliments acides (sauce tomate, vinaigre), aux nettoyants alcalins (NaOH) et aux cycles thermiques lors de la pasteurisation.
Utilisations courantes :
- Bandes transporteuses et rails de guidage
- Lames de coupe et composants de trancheuse
- Joints et joints pour machines de remplissage
- Ailettes d'échangeur de chaleur dans les pasteurisateurs laitiers
- Composants des équipements de brassage et de vinification
Conformité réglementaire avecFDA 21 CFR 178.3297,CE 1935/2004, et3-A Normes sanitairesest régulièrement vérifiée.
Applications dans le secteur médical
En technologie médicale, la biocompatibilité et la stérilisabilité du 316L le rendent adapté aux dispositifs jetables et implantables.
Applications clés :
- Composants d'instruments chirurgicaux (ciseaux, pinces)
- Ebauches d'implants orthopédiques (vis à os, plaques)
- Fils de guidage de cathéter et précurseurs de stents
- Membranes de capteurs de diagnostic
- Outillage dentaire et fils orthodontiques
Les bandes 316L électropolies réduisent les défauts de surface, minimisant la thrombogénicité et améliorant la durée de vie en fatigue, ce qui est essentiel pour les appareils cardiovasculaires.
Avantages par rapport aux alternatives
| Matériel |
Résistance à la corrosion |
Biocompatibilité |
Coût |
Magnétique? |
Limitations courantes |
| Acier inoxydable 316L |
Excellent |
Haut |
Moyen |
Non* |
Résistance inférieure par rapport aux alliages CoCr |
| 304 acier inoxydable |
Bon (pauvre en Cl⁻) |
Modéré |
Faible |
Non* |
Sujet aux piqûres dans une solution saline |
| Titane Grade 2 |
Excellent |
Excellent |
Haut |
Non |
Difficile à usiner/former |
| Alliage CoCr |
Excellent |
Excellent |
Très élevé |
Légèrement |
Fragile, cher |
| Aluminium |
Pauvre |
Faible |
Faible |
Non |
Ne convient pas aux environnements humides/acides. |
*Non magnétique à l'état recuit ; peut devenir légèrement magnétique après un travail à froid.
Le 316L atteint l'équilibre optimal entreperformances, fabricabilité et rentabilitépour les applications médicales et alimentaires moyen à haut de gamme.
Certifications de qualité et traçabilité
Des fournisseurs réputés fournissent :
- Rapports d'essais en usine (MTR) selon EN 10204 3.1 ou 3.2
- Données complètes des tests chimiques et mécaniques
- Traçabilité des lots (suivi du numéro de coulée)
- Certifications : ISO 13485 (médical), ISO 22000 (sécurité alimentaire), ASME BPE
Cela garantit une conformité totale avec les cadres réglementaires mondiaux et facilite les audits.
Conclusion
Les bandes d'acier inoxydable 316L / 1.4404 / SUS316L de haute précision (0,1 à 3,0 mm) représentent la référence en matière de composants fonctionnant dans les environnements les plus hygiéniques et corrosifs. Leur résistance exceptionnelle à la corrosion, renforcée par le molybdène, combinée à leur biocompatibilité, leur précision dimensionnelle et leur qualité de surface, les rend irremplaçables dans les équipements de transformation des aliments et les dispositifs médicaux qui sauvent des vies. Alors que les industries continuent d’exiger des matériaux plus propres, plus sûrs et plus fiables, les bandes d’acier inoxydable 316L resteront à l’avant-garde des solutions d’ingénierie avancées.




 Raian IonescuQualité matérielle très bonne. nous avons pour coopérer plus de 10 ans. Ils commercent des genres de sorts de matériel en acier. Toute la qualité matérielle bonne. Ils devoir pour toute la qualité matérielle. Nous surfaçons pour continuer à coopérer avec eux à l'avenir
Raian IonescuQualité matérielle très bonne. nous avons pour coopérer plus de 10 ans. Ils commercent des genres de sorts de matériel en acier. Toute la qualité matérielle bonne. Ils devoir pour toute la qualité matérielle. Nous surfaçons pour continuer à coopérer avec eux à l'avenir![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()