-
 Raian IonescuMaterial quality very good. we have cooperate more than 10 Years. They trade lots kinds of steel material. All material quality good. They duty for all material quality. We are planing continue cooperate with them in the future
Raian IonescuMaterial quality very good. we have cooperate more than 10 Years. They trade lots kinds of steel material. All material quality good. They duty for all material quality. We are planing continue cooperate with them in the future
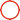
317L / S31703 Stainless Steel Plate Cold Rolled and Hot Rolled 0.6 - 30.0mm from TISCO
| Place of Origin | China |
|---|---|
| Brand Name | TISCO BAOSTEEL |
| Certification | ISO |
| Model Number | 317L / S31703 |
| Minimum Order Quantity | 500 kgs |
| Price | 5000 - 7200 USD/Ton |
| Packaging Details | standard packing for export |
| Delivery Time | 5 - 12 days based on the quantity |
| Payment Terms | T/T, Western Union |
| Supply Ability | 20Ton per week |

Contact me for free samples and coupons.
Whatsapp:0086 18588475571
Wechat: 0086 18588475571
Skype: sales10@aixton.com
If you have any concern, we provide 24-hour online help.
x| Products | Stainless Steel Plate | Grade | 317L / S31703 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness | 0.6 - 30.0mm | Width | 1219mm 1500mm 1800mm 2000mm |
| Surface | NO.1 2B | Brand | BAOSTEEL TISCO |
| Standard | ASTM A240/240M | Loading Port | Shanghai Port |
654SMO Stainless Steel Plate (UNS S32654, 1.4652) SS PlateThickness 1.0 - 80.0mm
Products Specification
| Products Name | 317L Stainless Steel Plate |
| Main Grades | Stainless Steel J1, J2, J4, 201, 202, 301, 304, 304H, 304L, 309, 309S, 310, 310S, 316, 316L, 316TI, 317L, 321, 321H, 347, 409, 410, 410S, 420, 430, 441, 904L,630,631,254SMO,654SMO,253MA,2205,2507.etc |
| Thickness | 0.6 - 30.0mm |
| Width | 1250mm,1500mm ,1800mm,2000mm, or custom other size as request |
| Length | 2000mm, 2440mm, 3000mm, 5800mm, 6000mm, AS PER CUSTOMER’S REQUIREMENT |
| Type of Material | Laser Cutting |
| Form | Plate / coil |
| Test Certificate | Yes. |
| Finish | NO.1, 2B, 2D, 2H, 2R, No.4, HAIRLINE, SCOTCH BRITE, SATIN FINISH, NO.8, BA. |
| Brand | TISCO, LISCO,BAOSTEEL , POSCO, JISCO |
Introduction to 317L Stainless Steel
317L stainless steel is a molybdenum-bearing, austenitic chromium-nickel stainless steel specifically designed to offer superior corrosion resistance, particularly in more aggressive environments compared to standard 316 or 316L grades. The "L" in its designation signifies its low carbon content (typically ≤ 0.030%), which significantly enhances its resistance to sensitization (chromium carbide precipitation at grain boundaries) and subsequent intergranular corrosion, especially after welding or exposure to high temperatures.
Key Characteristics & Advantages
-
Enhanced Corrosion Resistance: The defining feature of 317L is its higher molybdenum content (typically 3.0-4.0%) compared to 316L (2.0-3.0%). Molybdenum dramatically improves resistance to:
-
Pitting Corrosion: Especially in chloride-containing environments (e.g., seawater, chemical processing, coastal atmospheres).
-
Crevice Corrosion: In tight gaps where stagnant solutions can form.
-
General Corrosion: Particularly in sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), phosphoric acid (H₃PO₄), and other aggressive industrial chemicals.
-
Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC): Offers better resistance than 304/316 grades in many chloride environments, though not immune.
-
-
Low Carbon Content (L-Grade): The ≤ 0.030% C minimizes carbide precipitation during welding and high-temperature service, preserving corrosion resistance in the heat-affected zones (HAZ). This makes it readily weldable for fabricating tanks, pipes, and vessels.
-
Good Formability & Weldability: Retains the excellent formability and weldability characteristic of austenitic stainless steels (like 304/316). Common welding methods (TIG, MIG, MMA) are suitable. Post-weld annealing is generally not required due to the low carbon content.
-
High-Temperature Strength: Maintains good mechanical properties and oxidation resistance at elevated temperatures, though not primarily classified as a high-temperature alloy.
-
Non-Magnetic (Annealed Condition): Like other austenitic grades, it is essentially non-magnetic in the annealed state. Cold working can induce some magnetism.
Typical Chemical Composition (Weight %)
| Element | Min (%) | Max (%) | Key Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chromium (Cr) | 18.0 | 20.0 | Corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance |
| Nickel (Ni) | 11.0 | 15.0 | Austenite stability, formability, toughness |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 3.0 | 4.0 | Critical for pitting/crevice resistance |
| Manganese (Mn) | - | 2.0 | Austenite stability, deoxidizer |
| Silicon (Si) | - | 0.75 | Deoxidizer |
| Carbon (C) | - | 0.030 | Low carbon prevents sensitization |
| Phosphorus (P) | - | 0.045 | - |
| Sulfur (S) | - | 0.030 | - |
| Iron (Fe) | Balance | - | Base metal |
| Nitrogen (N) | - | 0.10 | Strengthener, austenite stabilizer |
*(Common specifications: ASTM A240, ASME SA-240; UNS S31703)*
Typical Mechanical Properties (Annealed Condition)
-
Tensile Strength (Rm): 515 MPa (min) - Typically 580-690 MPa
-
Yield Strength (Rp0.2): 170 MPa (min) - Typically 240-310 MPa
-
Elongation (% in 50mm): 40% (min) - Typically 45-55%
-
Hardness (Brinell): Typically 140-217 HB
-
Modulus of Elasticity: ~193 GPa (28 x 10^6 psi)
Pitting Resistance Equivalent Number (PREN)
A key indicator for comparing pitting resistance:
PREN = %Cr + (3.3 x %Mo) + (16 x %N)
For 317L, PREN typically ranges from 33 to 38, significantly higher than 316L (PREN ~24-29), confirming its superior resistance.
Common Applications
317L is used wherever standard 316/316L provides insufficient corrosion resistance, especially in environments containing chlorides or acids:
-
Chemical & Petrochemical Processing: Reactors, tanks, piping, heat exchangers, scrubbers handling sulfuric, phosphoric, acetic acids, and chlorides.
-
Pulp & Paper Industry: Digesters, bleaching equipment (chlorine dioxide environments).
-
Pollution Control (FGD - Flue Gas Desulfurization): Ducting, dampers, absorber towers exposed to wet SO₂ and chlorides.
-
Marine & Offshore Applications: Components requiring better pitting resistance than 316L in seawater or salt spray (e.g., pumps, valves, fasteners - though super duplex or Ni-alloys often preferred for critical parts).
-
Pharmaceutical Processing: Equipment requiring high corrosion resistance and cleanability.
-
Textile Processing: Equipment exposed to corrosive dyes and bleaches.
-
Food Processing: In aggressive environments where 316L might fail.
Important Considerations
-
Not for Marine Immersion: While better than 316L, it's generally not recommended for continuous immersion in seawater; super austenitic (e.g., 904L, 6% Mo alloys) or duplex/super duplex grades are usually preferred.
-
Sensitization Risk (Low, but present): Extremely prolonged exposure in the sensitization temperature range (approx. 425-870°C / 800-1600°F) can still pose a slight risk, though much lower than non-L grades.
-
Cost: Higher alloy content (especially Mo) makes it more expensive than 316L.
Summary
317L stainless steel is a versatile "upgraded" version of 316L, offering significantly improved pitting, crevice, and general corrosion resistance in aggressive chloride and acid environments, primarily due to its higher molybdenum content (3-4%) and low carbon level. Its excellent weldability and formability make it a crucial material for demanding applications in chemical processing, pollution control, and other industries where standard 316L might fail prematurely.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()